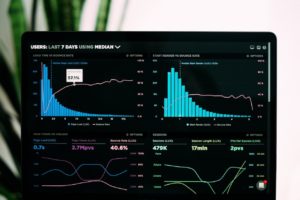
Our customers have access to monthly executive reports and can review ticketing reports real time when needed
An emerging shift in the IT industry is apparent with the ever-rising number of initiatives that introduce new digital technologies. It has transformed the role of a CIO, which was formerly about operating back-end technology to ensure machines ran at peak performance. A CIO is now expected to be leading the change behind IT business strategies, by directing their attention to cost-effective measures for delivering software solutions.
This means CIOs and other IT co-developers are participating more in responsibilities delegated to management boards. IT departments are gaining traction as value generators for the organization by preventing server shutdowns, power outages, HR databases, SaaS applications, and other technical difficulties a company will face at some point. IT monitors all the shared cloud drives that support devices from laptops to smartphones.
Why IT Leaders are Struggling During Performance Reports about Invested Technology
But when it comes to reporting, many IT leaders had trouble explaining their team’s contributions to the CEO and board of executives. The problem stems from a pervasive mindset that IT budgets should be restricted to only maintaining company infrastructure rather than investing in upgrades for speeding up internal communication networks. IT leaders must prove their worth by addressing why IT is one of the main components of executing a successful business model.
Here are the main criterion used in IT reporting as per business impact:
1. The frequency of power outages in a period-These could compromise security measures, enterprise programs, or CRM systems. IT must fix them before a loss in revenue occurs.
2. Percentage of incidents resolved by an in-house IT team-This includes quantified data about technical issues and their potential costs. Speed and accuracy are the main benchmarks.
3. The integrity of IT transactions-An organization relies on platforms that manage multiple applications, namely HR, order-entry, and ERP systems, making sure transactions run smoothly on any device.
4. The number of permanently fixed problems-The IT staff is assigned damage control whenever an organization encounters recurring incidents. Long-lasting, automated solutions will raise its workforce productivity.
5. A follow-up change management summary-After documenting changed processes, IT leaders must submit a detailed overview of their impact analysis and write up a rollout plan in response.
6. Service levels and their availability-IT leaders will also keep tabs on their help desk services. They’re expected to record service level achievements while regularly updating all of their operating systems in favor of business objectives.
Outlining a Template Suitable for IT Monthly Management Reports
An IT management report informs organizations about recent trends in cloud computing, internet of things, and big data analytics. In addition, this report provides them with oversight into different areas of operation, and through proper guidelines, the key points, elements, or features essential to IT functions. After all, you need to know the objective of a workplace investigation before you can begin.
Furthermore, be specific with the terms used in the IT report so that people who review it can understand what kind of open database standards were applied. Every piece of information should be credible and updated on systems with administrative access. Only appoint people with the right skills and expertise to create an IT management report. Another suggestion is to present visual infographics and factual statistics or figures in an easy-to-read format.
IT Management Reporting-A Monthly Inspection of Company Databases
Being prepared with all the equipment and resources is vital in order to present a credible report. Moreover, you’re required to install automated feedback generating IT systems which prioritize research and troubleshooting activities. You may have to deal with elements like hardware for assessment functions and develop a corrective action report based on the measures taken to meet business expectations.
An IT management report must generate value by supplying data management could rely on for better decision-making. If changes must be implemented in IT, then management must check that they are contributing to the company instead of piling on excess expenditures. Always be well-organized when putting together the contents to elicit meaningful discussions about the company’s IT infrastructure.
Contact us at SystemsNet to browse our managed IT services including remote repairs. We will monitor your existing hardware and write up a monthly report on your network capabilities.